FEATURE | Australia’s east coast gas market – What’s the role for LNG imports?

Australia is close to becoming the largest LNG exporter in the world. At the same time, there were four proposed terminals on the east coast of Australia. What’s the role for LNG imports in this context?
A combination of volatile gas demand, declining mature gas fields and LNG exports will point to possible gas shortages where gas is consumed most in Australia: on the east coast.
Further complicating matters, the domestic market is already in direct competition with the Queensland LNG projects for east coast gas.
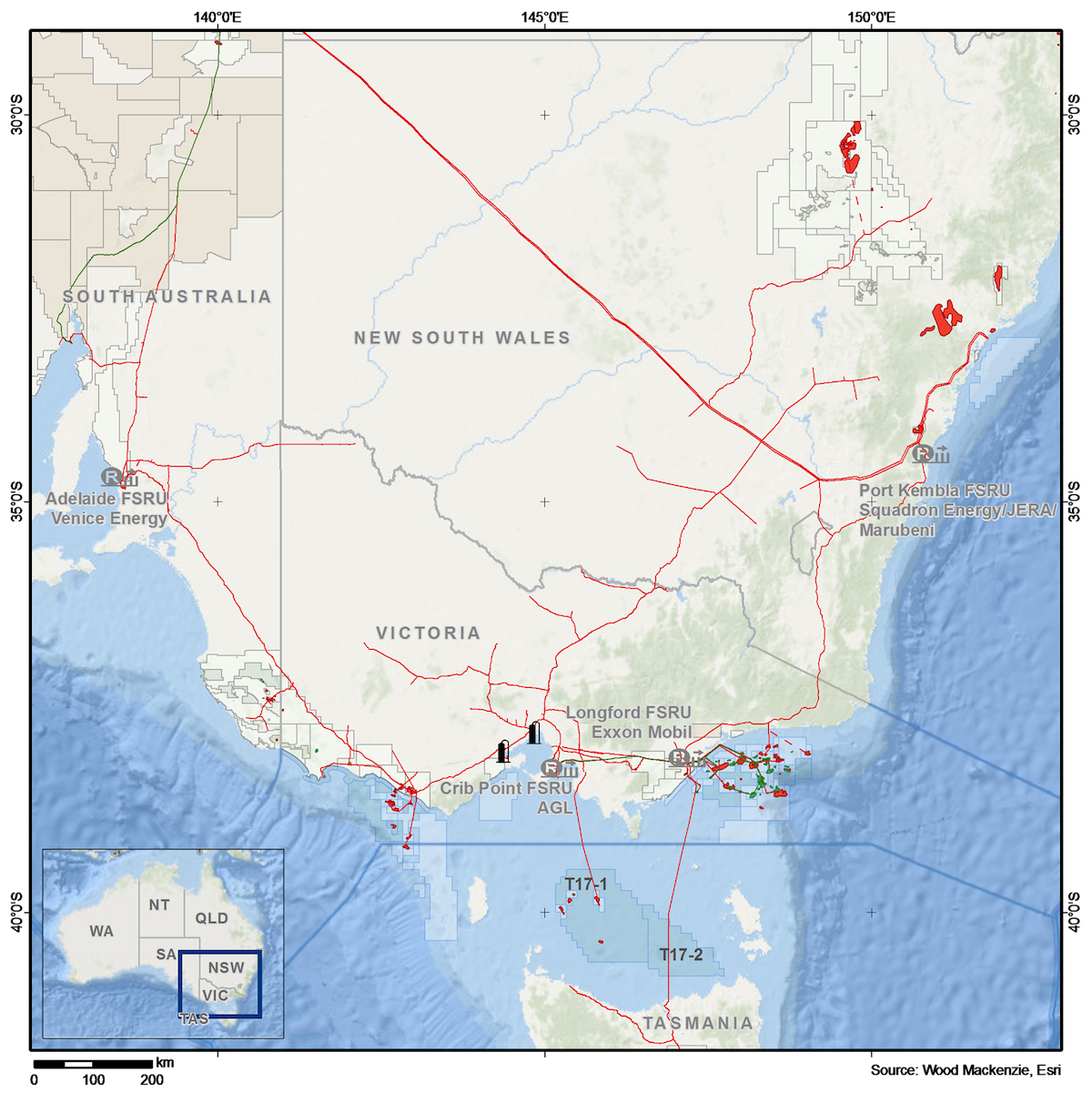 Proposed Australian regas terminals
Proposed Australian regas terminals
Traditional east coast reserves such as the Gippsland Basin are depleting and production is set to decline. Unless significant new reserves are commercialised, within five to seven years, the east coast market comprising the eastern and southern states of Queensland, New South Wales, Victoria and South Australia will be short of gas.
The market will then need to draw on the massive coal seam gas (CSG) reserves of Queensland. However, these reserves are mostly dedicated to the three LNG export projects: APLNG, QCLNG and GLNG.









